Imagine an ecosystem where your refrigerator, thermostat, and factory floor sensors are part of a single, supremely efficient organism – this is the brave new world brought to life by IoT innovation. In a time when your toaster might have Wi-Fi and your fridge manages your grocery list, IoT has quietly become mainstream. Today’s tiny devices are revolutionizing daily life, whether you’re tracking your morning jog or monitoring factory equipment – the advantages are staggering.
Rapid growth has a darker side: new vulnerabilities emerge with each incremental step. Every device you bring into your home or office silently invites potential cyber threats to the party. Though it may sound amusing to think of a hacker hijacking your smart lightbulb, the risks become real—and concerning—once you realize that every connected device is part of a larger network. This is where IoT software development comes in. The recent goal for developers is safeguarding digital infrastructure by engineering reinforced encryption strategies and streamlined security practices. Your smart doorbell may be conveniently connected, but is it a soft target for crooks? Let’s get the lowdown on the latest IoT security advancements.
1. Edge Computing and Its Role in IoT Security
The biggest shift in IoT security today is the move toward edge computing. In simple terms, edge computing shifts the processing power from distant cloud servers to closer, device-level locations. Why is this important? Imagine trying to stop a burglar, but you have to run across town to the police station before sounding the alarm. By the time help arrives, the burglar is long gone with your smart vacuum. Now, picture having a security guard on your street corner—that’s edge computing. Processing data near the device allows for quicker detection and response to threats.
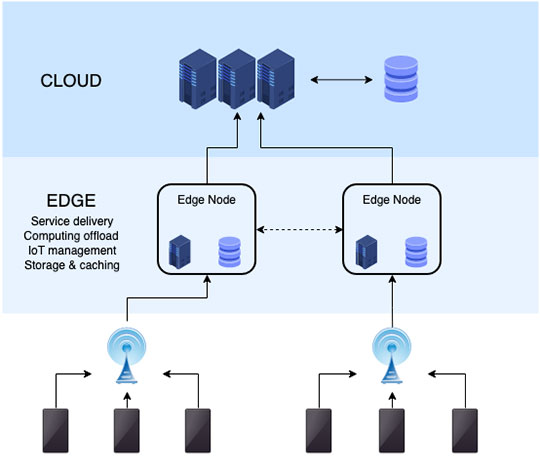
More critically, edge computing limits the exposure of sensitive data to the cloud, where it’s often vulnerable. By processing information locally, devices can enforce stronger security measures, essential for industries like healthcare and financial services, where privacy is paramount.
2. Improved Device Authentication
One critical area where IoT devices must improve is verifying their identities. Think of it like a digital ID card—just because your fitness tracker says it’s part of your network doesn’t mean it’s not an imposter in disguise. The thing that’s really stolen the spotlight in IoT security lately is the whole device authentication issue.
Device authentication ensures that the connected gadget is legitimate and that no rogue devices slip through. Blockchain technology stands out as a particularly fascinating development in this area. Envision a secure, digital fingerprint for each device, stored in a virtual archive that’s tamper-proof and transparent. Blockchain significantly increases the difficulty for hackers in replicating or tampering with devices. The buzz around blockchain in IoT security is mounting, and for good reason – its transparent nature and intrinsic security are a powerful combo.
Another method is using multi-factor authentication for devices, kind of like when you get a code sent to your phone to verify your identity when logging into a website. A layered defense is always better—whether you’re protecting your email account or your smart thermostat.
3. AI-Powered Threat Detection
IoT devices often lack the processing power to run traditional, resource-heavy security protocols, which is where artificial intelligence (AI) becomes crucial. AI-powered security tools can quickly analyze vast data streams, detecting unusual patterns and potential threats that humans might miss.
Acting like a digital watchdog, AI continuously monitors devices, identifying suspicious behavior in real-time. Machine learning enhances this process, allowing systems to learn what constitutes normal activity for each device, flagging any irregularities—whether it’s strange data being sent to an unknown server or your smart speaker making unusual purchases.
4. Zero Trust Architecture
The term “zero trust” might sound a bit like the premise of a bad spy movie, but when it comes to IoT security, it’s a crucial development. The zero trust model assumes that no device, person, or application should be trusted by default—whether it’s inside or outside the network. Every interaction is verified, authenticated, and continuously monitored.
In an IoT context, this is essential. IoT devices often interact with other systems, software, and networks, creating multiple potential points of vulnerability. A zero-trust framework requires strict identity verification and grants access only to those who are explicitly authorized.
Think of it as the security guard in your smart neighborhood who checks everyone’s ID, regardless of whether they claim to be your friendly neighbor. It might feel a little paranoid, but in the world of IoT, a healthy dose of skepticism goes a long way in keeping things secure.
5. Firmware Security Updates: Easier Said Than Done
Ask anyone with a smart device about updates, and you’ll likely get an eye-roll and a story about their smart fridge going offline after a failed firmware update.
Keeping IoT devices secure requires regularly updating their firmware to fix security vulnerabilities. Simple enough, right? Not quite. Many IoT devices have limited processing power, making updates tricky. Worse still, users often ignore update notifications (we’ve all hit “Remind me later” too many times).
Skipping updates leaves devices vulnerable to attacks exploiting outdated software. To address this, manufacturers are pushing for automated updates that reduce or remove the need for user action.
With these advances, you’ll no longer worry about your smart coffee maker being hacked just because you forgot to press “Install.”
Final Thoughts
The rapid growth of IoT ecosystems brings significant challenges in securing the vast number of connected devices. Major advancements like edge computing and AI-powered threat detection are transforming IoT protection by offering quicker responses and smarter defenses. Zero trust architecture and blockchain-based authentication are strengthening network integrity, ensuring that every device and interaction is verified.
Additionally, automated firmware updates help reduce human error and make security measures more consistent. By adopting these technologies, industries can better protect their IoT networks from increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, safeguarding both data and privacy.
Thomas Hyde
Related posts
Popular Articles
Best Linux Distros for Developers and Programmers as of 2024
Linux might not be the preferred operating system of most regular users, but it’s definitely the go-to choice for the majority of developers and programmers. While other operating systems can also get the job done pretty well, Linux is a more specialized OS that was…
How to Install Pip on Ubuntu Linux
If you are a fan of using Python programming language, you can make your life easier by using Python Pip. It is a package management utility that allows you to install and manage Python software packages easily. Ubuntu doesn’t come with pre-installed Pip, but here…











